Biomolecular condensates: from biology towards materials
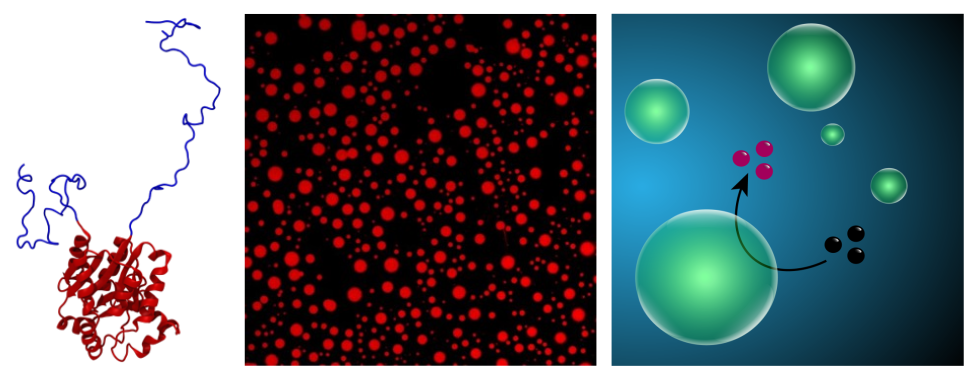
Biomolecular condensates are emerging as a smart strategy evolved by cells to coordinate reactions in space and time. We aim to recapitulate this class of liquid-liquid phase separated compartments in biotechnology to generate adaptve materials and microreactors, capable to change their composition and material properties in response to external stimuli. These programmable compartments could find applications in many areas of drug discovery, delivery and manufacturing, as well as in chemical synthesis.
Contacts
Condensates for separation and diagnostics: Jonathan, Marianna, Roberto, Niccoló, Nils
Key publications
external page Stoffel et al. "Enhancement of enzymatic activity by biomolecular condensates through pH buffering" Nat Commun, 2025.
external page Gil-Garcia et al. "Local environment in biomolecular condensates modulates enzymatic activity across length scales"Nat Commun, 2024.
external page U. Capasso Palmiero et al. 'Programmable Zwitterionic Droplets as Biomolecular Sorters and Model of Membraneless Organelles" Advanced Materials,2022
external page A.M. Küffner et al. "Acceleration of an Enzymatic Reaction in Liquid Phase Separated Compartments Based on Intrinsically Disordered Protein Domains" ChemSystemsChem, 2020
external page U. Capasso Palmiero et al. 'Adaptive Chemo-enzymatic Microreactors Composed of Inorganic Nanoparticles and Bio-inspired Intrinsically Disordered Proteins" Angewandte Chemie Int. Ed., 2020